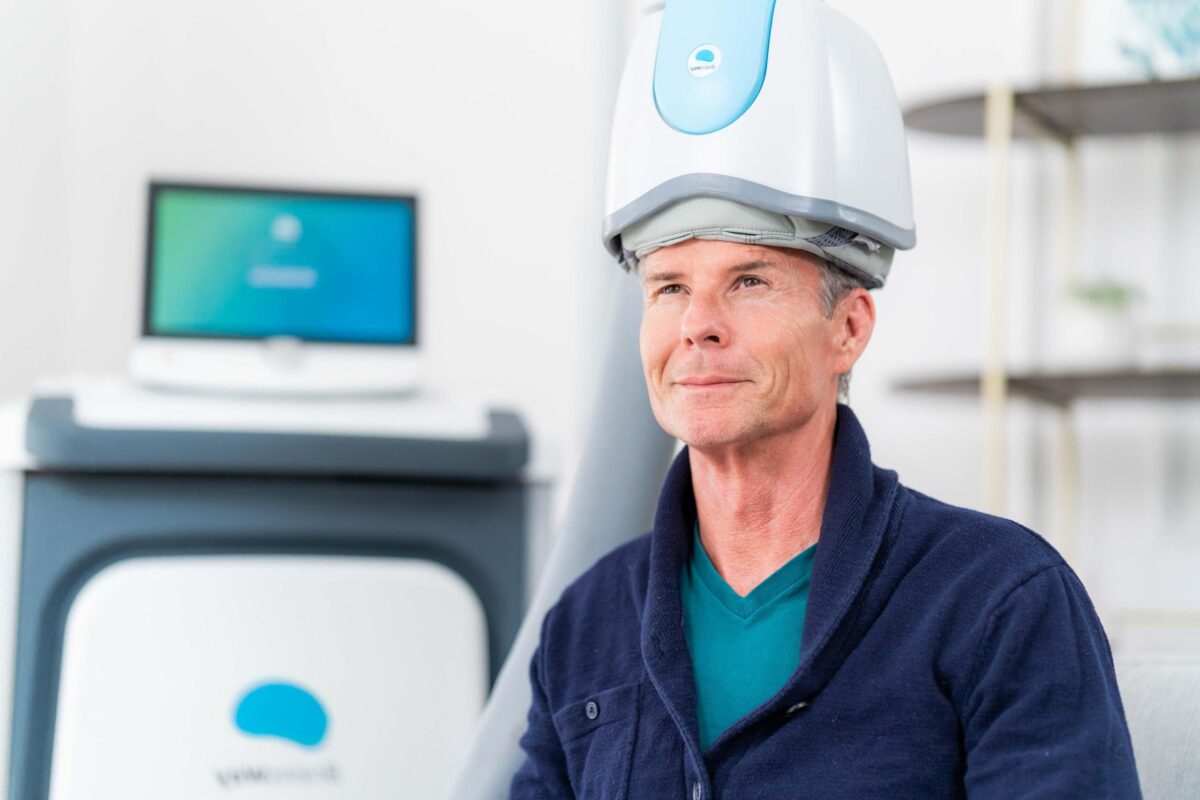
Addiction is a complex condition that impacts the brain’s reward, motivation, and decision-making circuits. Many who struggle with addiction feel trapped in a cycle of dependency, even as they work through traditional treatments like counseling, support groups, and medications. While these methods have helped countless individuals achieve recovery, they don’t work for everyone. For those seeking an innovative and non-invasive approach, Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) offers new hope.
TMS is a treatment that uses magnetic fields to stimulate specific areas of the brain, modulating neural activity in regions associated with addiction. Its application to addiction recovery is relatively recent, yet growing research suggests it may offer a valuable alternative or supplement to traditional addiction treatments.
Understanding TMS and How It Works
TMS involves the placement of a magnetic coil on the scalp, which delivers focused magnetic pulses to targeted areas of the brain. These pulses can alter neural activity by increasing or decreasing brain cell excitability, effectively resetting patterns of brain activity. Unlike medications that act systemically, TMS directly targets specific areas of the brain, allowing for a highly focused approach.
One of the primary targets of TMS for addiction is the prefrontal cortex, a region associated with decision-making, impulse control, and reward processing. In individuals with addiction, this area of the brain often becomes dysregulated, making it difficult to resist cravings or make sound decisions. By stimulating this region, TMS aims to rebalance brain activity and restore healthier neural patterns, helping to reduce compulsive behaviors and improve self-control.
The Link Between Brain Activity and Addiction
Addiction is more than a behavioral issue; it is deeply rooted in the brain’s structure and function. When someone develops an addiction, their brain undergoes physical and chemical changes that reinforce dependency and make it hard to break the cycle. Brain imaging studies have shown that individuals with addiction often experience heightened activity in the reward pathways and diminished activity in the prefrontal cortex, which is essential for self-regulation and impulse control.
The overactivation of the reward pathway means that cues associated with substance use—such as certain environments, people, or emotional states—can trigger intense cravings, making relapse more likely. At the same time, reduced activity in the prefrontal cortex limits a person’s ability to resist these urges. This imbalance creates a cycle where reward-seeking behaviors become hardwired, and self-control becomes compromised. TMS offers a way to modulate these brain circuits, aiming to weaken the brain’s response to addictive triggers and strengthen areas involved in restraint and decision-making.
TMS as an Alternative to Traditional Treatments
Traditional addiction treatments, while effective for many, have limitations. Counseling and support groups provide essential psychological support but may not directly address the neurological components of addiction. Medications can help manage withdrawal symptoms and cravings, yet they often come with side effects and may not be suitable for everyone.
TMS offers a different approach by directly targeting the neural mechanisms of addiction. This non-invasive treatment does not rely on medication, making it an appealing option for those who prefer to avoid pharmaceuticals. Furthermore, TMS has few side effects, most of which are mild and temporary, such as headaches or scalp discomfort. Since it doesn’t require recovery time, patients can resume their regular activities immediately after each session, making it convenient for those balancing treatment with work or family responsibilities.
Research on TMS and Addiction
While TMS has gained recognition for its success in treating depression, research on its application to addiction is still emerging. However, early studies are encouraging. In one study, participants with alcohol use disorder who underwent TMS reported fewer cravings and greater control over their impulses compared to those who received a placebo treatment. Similar studies focusing on nicotine and cocaine addiction have found that TMS can reduce cravings and help individuals maintain sobriety for longer periods.
One of the key findings from these studies is that TMS appears to reduce the brain’s sensitivity to drug-related cues. For example, after TMS sessions, individuals exposed to cues like the sight of a cigarette or the smell of alcohol were less likely to experience intense cravings. This reduction in cue-induced cravings is a promising outcome, as these triggers are often responsible for relapse.
Another significant finding is that TMS may improve cognitive function in individuals with addiction, enhancing abilities like working memory, attention, and decision-making. These cognitive benefits can be crucial in supporting long-term recovery, as better mental functioning equips individuals to manage stress and avoid situations that may lead to relapse.
What to Expect During TMS Treatment for Addiction
For those interested in TMS as part of addiction treatment, understanding the process can help demystify the experience. Each TMS session typically lasts between 30 and 60 minutes, depending on the treatment protocol. Patients remain seated and fully awake, with a magnetic coil placed on their scalp near the targeted brain area. They may feel a light tapping sensation on their scalp, but the procedure is generally well-tolerated and requires no anesthesia or sedation.
Treatment usually involves multiple sessions over several weeks. This repeated stimulation is essential for creating lasting changes in brain activity, as the cumulative effect of TMS is what leads to symptom relief and improved cognitive function. Many patients begin to notice changes in cravings and impulse control after a few weeks, but individual responses can vary.
Combining TMS with Other Treatment Approaches
For most individuals, a comprehensive approach to addiction recovery is ideal. TMS can be an effective standalone treatment, but it may work best when combined with other methods, such as counseling or behavioral therapies. Combining TMS with psychotherapy, for example, allows individuals to address both the neurological and psychological aspects of addiction. While TMS helps recalibrate brain activity, therapy can help patients build healthier coping strategies and develop resilience.
TMS can also complement medication-assisted treatment (MAT) for those using medications to manage withdrawal or cravings. Since TMS is non-pharmacological, it does not interfere with medications and may even enhance their effectiveness by targeting underlying neural patterns.
The Future of TMS in Addiction Treatment
As research on TMS and addiction continues, scientists are exploring new ways to optimize treatment protocols. Studies are looking into the ideal frequency, duration, and intensity of TMS sessions for various types of addiction, aiming to personalize the approach based on individual needs. There is also ongoing research into combining TMS with advanced brain imaging techniques to monitor changes in brain activity over time, allowing clinicians to adjust treatments more effectively.
Another promising area of research is the use of TMS in treating behavioral addictions, such as gambling, internet addiction, and food addiction. Although these addictions do not involve substances, they share similar neural pathways with substance-related addictions. TMS’s ability to regulate brain activity could make it a useful tool for these conditions as well.
Moving Forward with TMS for Addiction
For individuals who feel they have exhausted traditional treatment options or are seeking a non-invasive, drug-free approach, TMS offers a promising avenue. By directly targeting the brain circuits involved in addiction, TMS provides a unique method for reducing cravings, strengthening impulse control, and supporting cognitive health—all key factors in achieving long-term recovery.
If you or a loved one is considering TMS for addiction, consulting with a healthcare provider experienced in brain stimulation therapies can provide further insight into its suitability for your needs. While TMS may not be a cure-all, its potential to transform addiction treatment marks a significant advancement, bringing new hope for those on the path to recovery. For more information on TMS and other innovative treatments, visit Axon Integrative Health.